GEOGRAPHY OF CAMBODIA
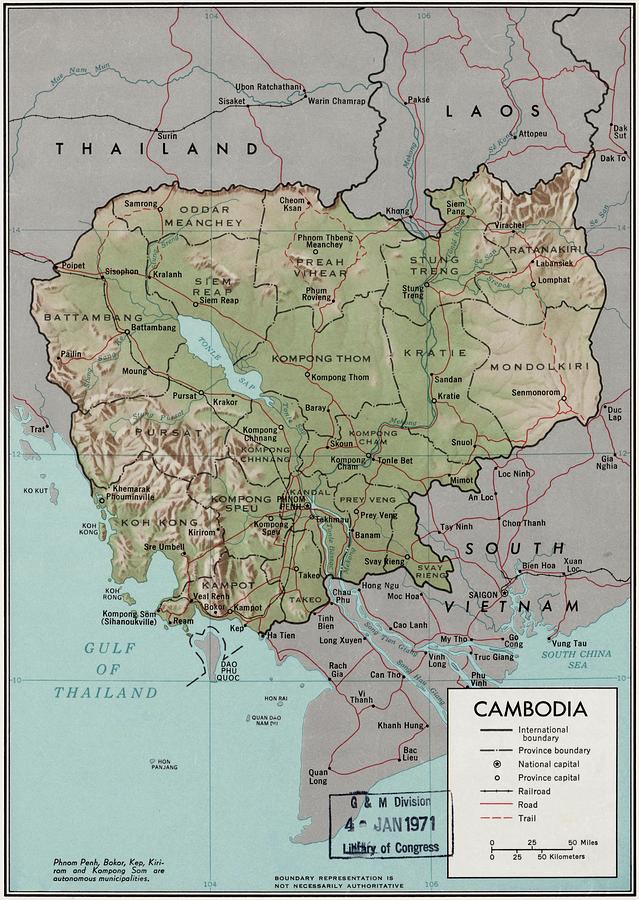
Cambodia is a country in mainland Southeast Asia, border Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, the Gulf of Thailand and covers a total area of 181,035 km2 (69,898 sq mi). The country is situated in its entirety inside the tropical Indomalaya realm and the Indochina Time zone (ICT).
Cambodia's main geographical features are the low-lying Central Plain that includes the Tonlé Sap basin, the lower Mekong River flood-plains and the Bassac River plain surrounded by mountain ranges to the north, east, in the south-west and south. The central lowlands extend into Vietnam to the south-east. The south and south-west of the country constitute a 443 km (275 mi) long coast at the Gulf of Thailand, characterized by sizable mangrove marshes, peninsulas, sandy beaches and headlands and bays. Cambodia's territorial waters account for over 50 islands. The highest peak is Phnom Aural, sitting 1,810 meters (5,938 ft) above sea level.
The landmass is bisected by the Mekong River, which at 486 km (302 mi) is the longest river in Cambodia. After extensive rapids, turbulent sections and cataracts in Laos, the river enters the country at Stung Treng province, is predominantly calm and navigable during the entire year as it widens considerably in the lowlands. The Mekong's waters disperse into the surrounding wetlands of central Cambodia and strongly affect the seasonal nature of the Tonlé Sap lake.
Two third of the country's population live in the lowlands, where the rich sediment deposited during the Mekong's annual flooding makes the agricultural lands highly fertile. As deforestation and over-exploitation affected Cambodia only in recent decades, forests, low mountain ranges and local eco-regions still retain much of their natural potential and although still home to the largest areas of contiguous and intact forests in mainland Southeast Asia, multiple serious environmental issues persist and accumulate, which are closely related to rapid population growth, uncontrolled globalization and inconsequential administration.
The majority of the country lies within the Tropical savanna climate zone, as the coastal areas in the South and West receive noticeably more and steady rain before and during the wet season. These areas constitute the easternmost fringes of the south-west monsoon, determined to be inside the Tropical monsoon climate. Countrywide there are two seasons of relatively equal length, defined by varying precipitation as temperatures and humidity are generally high and steady throughout the entire year.
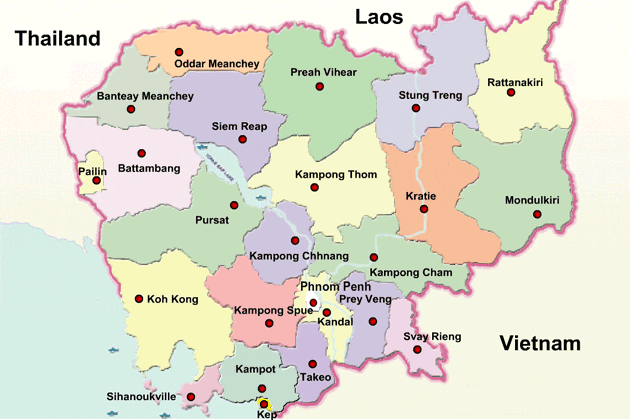
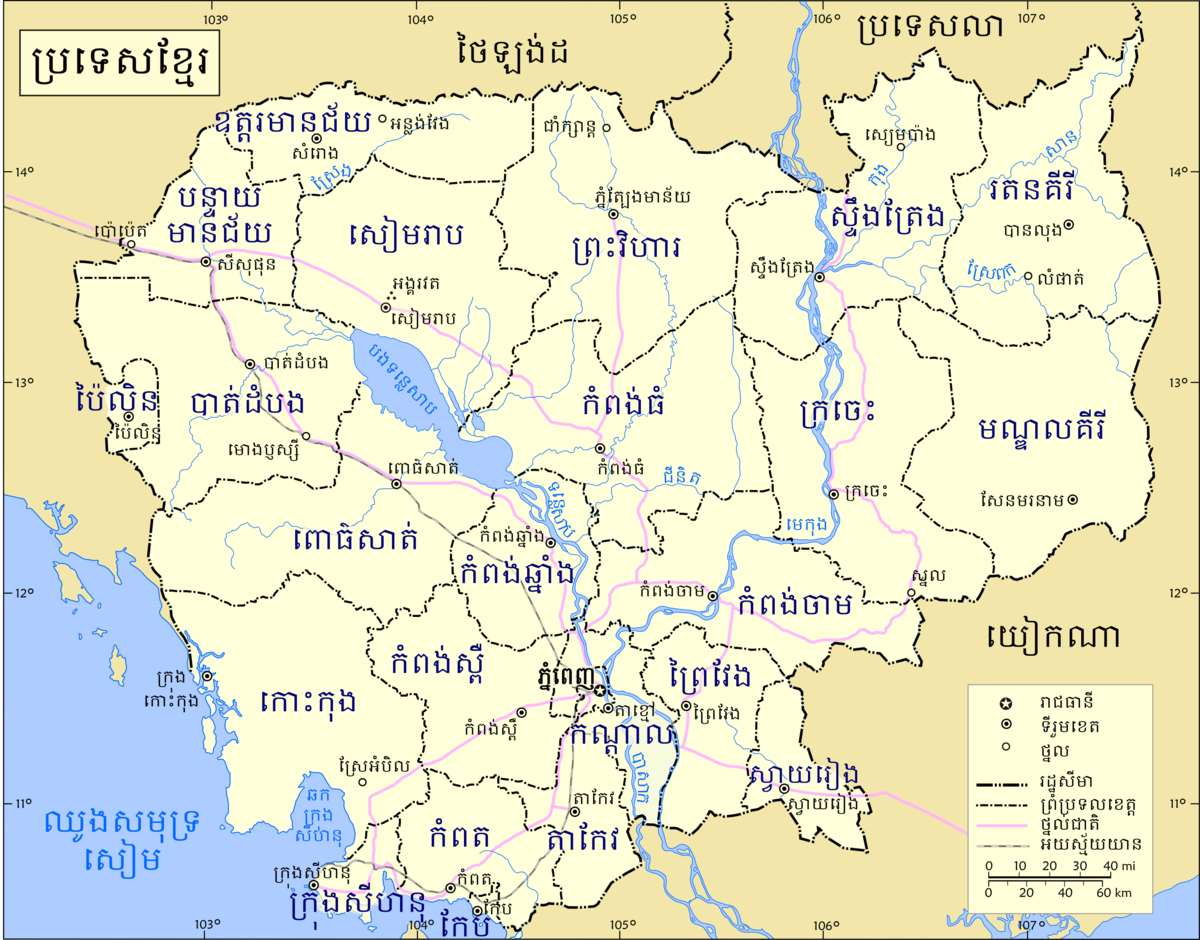
Cambodia is divided into 25 provinces (Khmer: ខេត្ត, khaet, singular and plural). The capital Phnom Penh is not a province but an "autonomous municipality", equivalent to a province governmentally and administered at the same level as the other 24 provinces.
Phnom Penh has both the highest population and the highest population density of all provinces, but is the second smallest in land area. The largest province by area is Mondulkiri and the smallest is Kep which is also the least populated province. Mondulkiri has the lowest population density.
Each province is administered by a governor, who is nominated by the Ministry of Interior, subject to approval by the prime minister.
Provinces are divided into districts (srok, Khmer: ស្រុក) / Khan (Khmer: ខណ្ឌ). The districts of Phnom Penh are called khan, normally written as Khan for addresses in English. The number of districts in each province varies, from two in the smallest provinces to 14 in Battambang, Prey Veng, and Siem Reap. Further subdivision levels are khum (Khmer: ឃុំ, communes) or sangkat (Khmer: សង្កាត់, quarters) and finally, phum (Khmer: ភូមិ, villages). In Phnom Penh, Sangkat is used in the place of Khum and, similar to Khan, normally preferred as Sangkat for addresses in English.
Climate
Cambodia's climate, like that of much of the rest of mainland Southeast Asia is dominated by monsoons, which are known as tropical wet and dry because of the distinctly marked seasonal differences. The monsoonal air-flows are caused by annual alternating high pressure and low pressure over the Central Asian landmass. In summer, moisture-laden air—the southwest monsoon—is drawn landward from the Indian Ocean.
The flow is reversed during the winter, and the northeast monsoon sends back dry air. The southwest monsoon brings the rainy season from mid-May to mid-September or to early October, and the northeast monsoon flow of drier and cooler air lasts from early November to March. Temperatures are fairly uniform throughout the Tonlé Sap Basin area, with only small variations from the average annual mean of around 25 °C (77.0 °F).
The maximum mean is about 30 °C (86 °F); the minimum mean, about 24 °C (75 °F). Maximum temperatures of higher than 32 °C (90 °F), however, are common and, just before the start of the rainy season, they may rise to more than 38 °C (100 °F). Minimum night temperatures sporadically fall below 20 °C (68 °F). in January, the coldest month. May is the warmest month - although strongly influenced by the beginning of the wet season, as the area constitutes the easternmost fringe of the south-west monsoon. Tropical cyclones only rarely cause damage in Cambodia.
The total annual rainfall average is between 1,000 and 1,500 mm (39.4 and 59.1 in), and the heaviest amounts fall in the southeast. Rainfall from April to September in the Tonlé Sap Basin-Mekong Lowlands area averages 1,300 to 1,500 mm (51.2 to 59.1 in) annually, but the amount varies considerably from year to year. Rainfall around the basin increases with elevation. It is heaviest in the mountains along the coast in the southwest, which receive from 2,500 mm (98.4 in) to more than 5,000 mm (196.9 in) of precipitation annually as the southwest monsoon reaches the coast.
This area of greatest rainfall drains mostly to the sea; only a small quantity goes into the rivers flowing into the basin. Relative humidity is high throughout the entire year; usually exceeding 90%. During the dry season daytime humidity rates average around 50 percent or slightly lower, climbing to about 90% during the rainy season.

FOR MORE DETAILS: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geography_of_Cambodia
REFERENCE: wikipedia.org
No comments:
Post a Comment